文章来源:Ouping Deng, Sitong Wang, Jiangyou Ran, Shuai Huang, Xiuming Zhang, Jiakun Duan, Lin Zhang, Yongqiu Xia, Stefan Reis, Jiayu Xu, Jianming Xu, Wim de Vries, Mark A. Sutton & Baojing Gu. (2024). Managing urban development could halve nitrogen pollution in China. Nature Communications: 15, 401. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-44685-y.
整理人:徐嘉苗,2021级本科生
整理时间:2024年6月3日
Abstract: Halving nitrogen pollution is crucial for achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). However, how to reduce nitrogen pollution from multiple sources remains challenging. Here we show that reactive nitrogen (Nr) pollution could be roughly halved by managed urban development in China by 2050, with NH3, NOx and N2O atmospheric emissions declining by 44%, 30% and 33%, respectively, and Nr to water bodies by 53%. While rural-urban migration increases point-source nitrogen emissions in metropolitan areas, it promotes large-scale farming, reducing rural sewage and agricultural non-point-source pollution, potentially improving national air and water quality. An investment of approximately US$ 61 billion in waste treatment, land consolidation, and livestock relocation yields an overall benefit of US$ 245 billion. This underscores the feasibility and cost-effectiveness of halving Nr pollution through urbanization, contributing significantly to SDG1 (No poverty), SDG2 (Zero hunger), SDG6 (Clean water), SDG12 (Responsible consumption and production), SDG14 (Climate Action), and so on.
摘要:将氮污染减半对于实现可持续发展目标(SDGs)至关重要。然而,如何减少来自多源的氮污染仍然是一项挑战。我们发现到2050年通过中国有序的城市发展可将活性氮(Nr)污染大致可以减半,其中NH3、NOx和N2O的大气排放分别下降44%、30%和33%,进入水体的Nr减少53%。尽管城乡迁移加剧了大都市区点源氮排放,但它促进了大规模农业的发展,减少了农村污水和农业非点源污染,有望改善国家空气和水质。在废物处理、土地整治和畜禽迁移方面的投资约为610亿美元,总体收益可达2450亿美元。这强调了通过城市化途径减半Nr污染的可行性和成本效益,极大地促进了SDG1(无贫穷)、SDG2(零饥饿)、SDG6(清洁水源)、SDG12(负责任消费和生产)、SDG13(气候行动)等目标的实现。
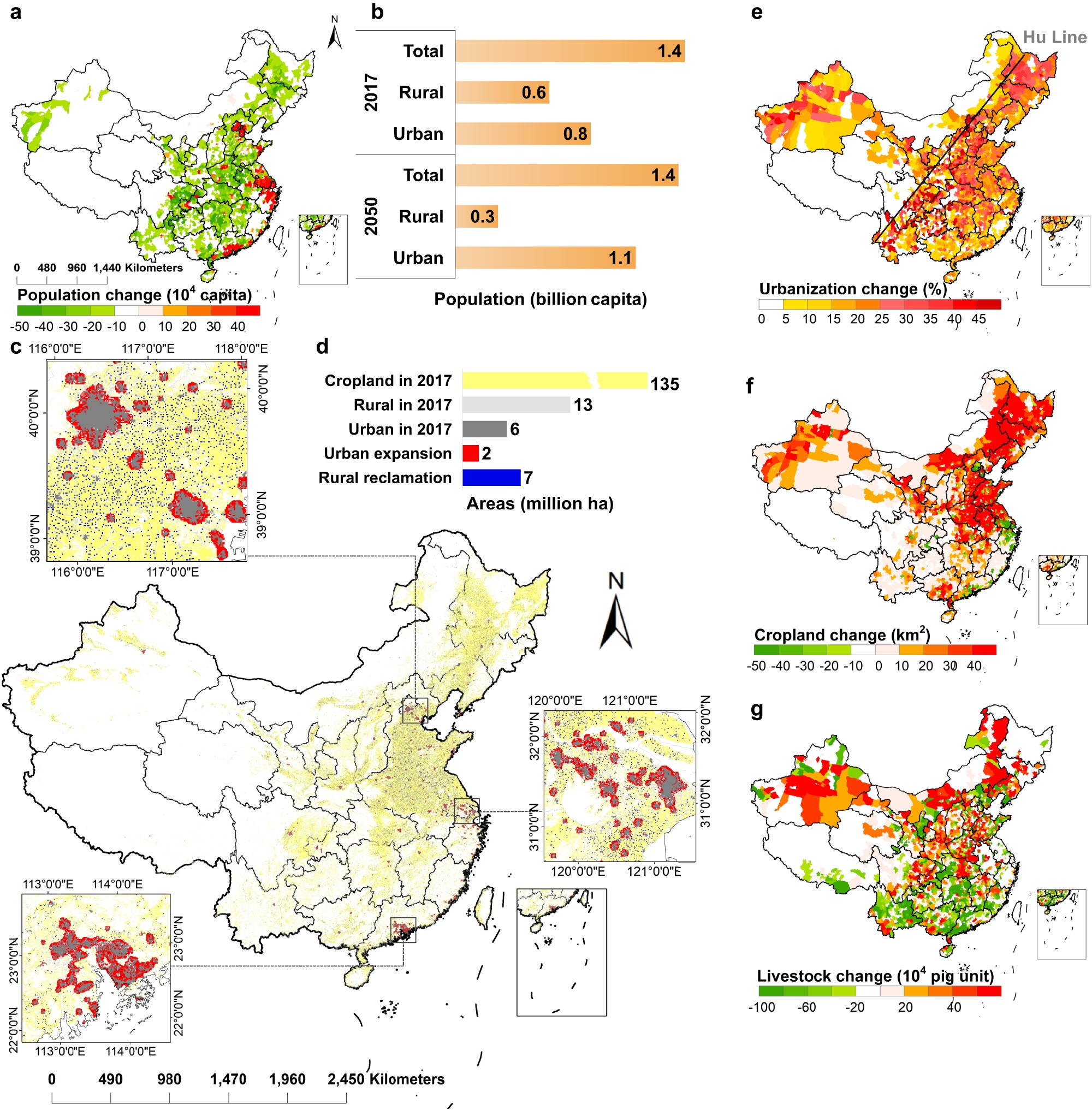
图 城市化带来的人口、土地利用和农业变化
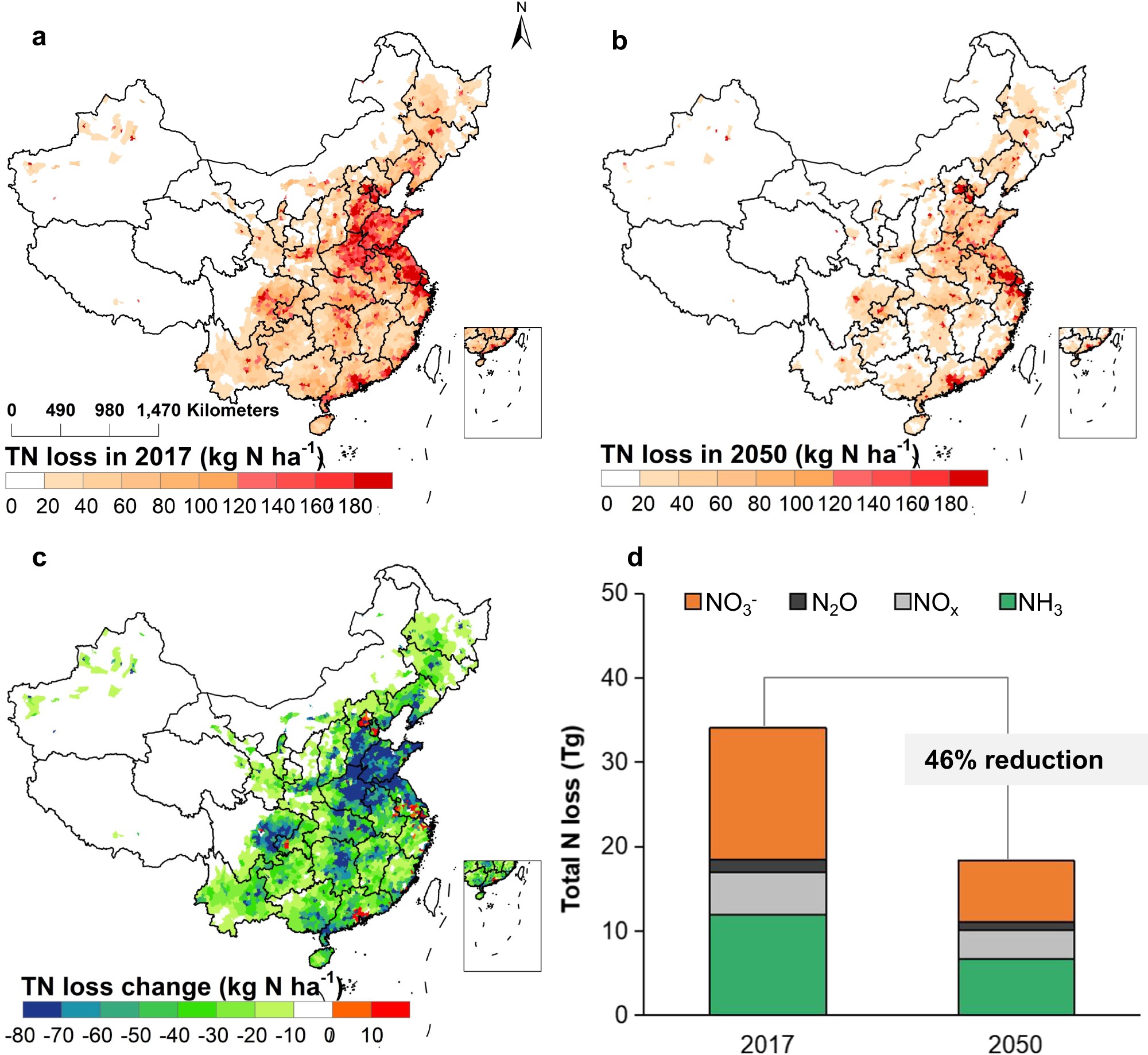
图 氮损失随城市化的空间变化

图 关键子系统内的氮预算及其对城市化减少氮损失的贡献
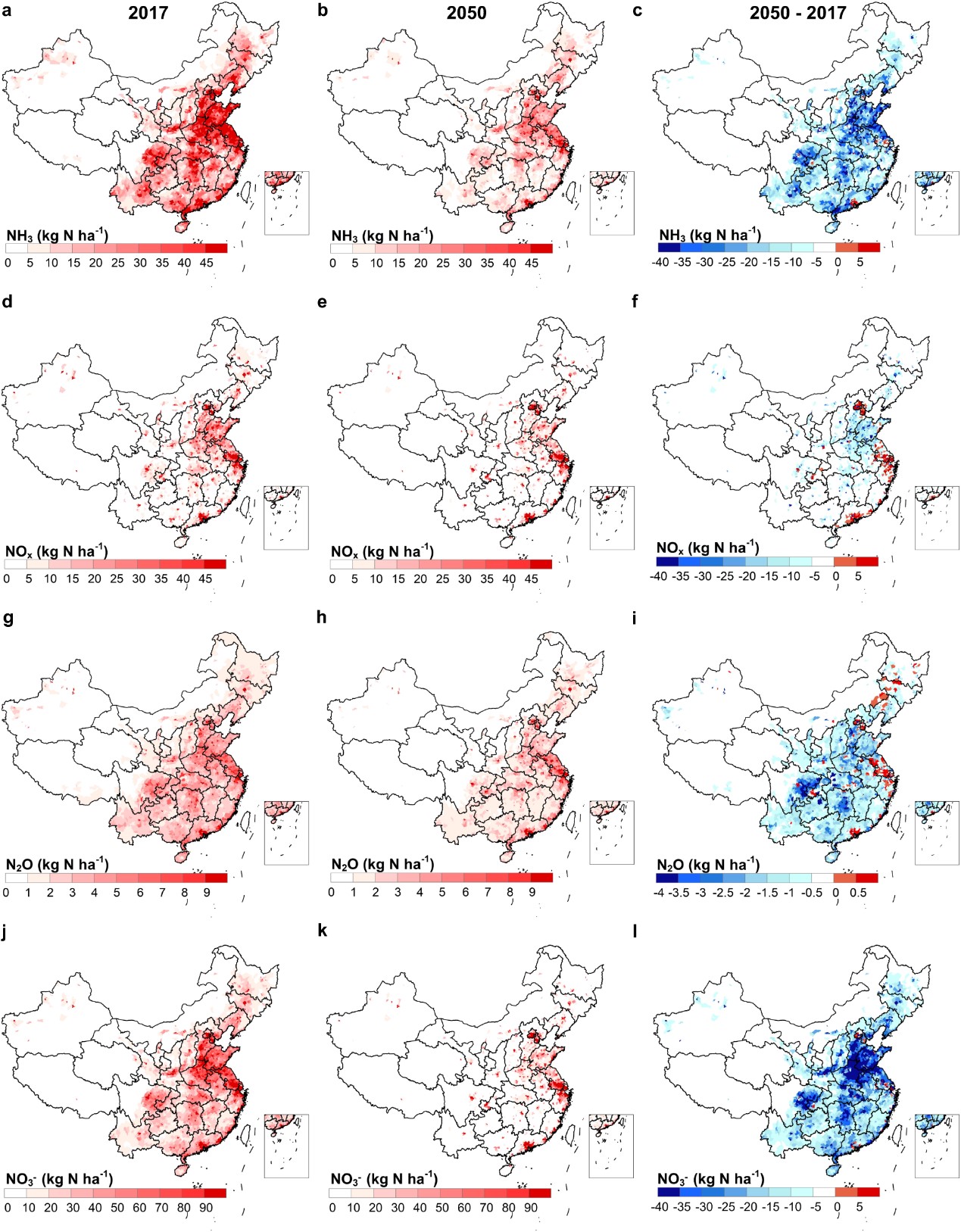
图 活性氮随城市化消失的空间变化
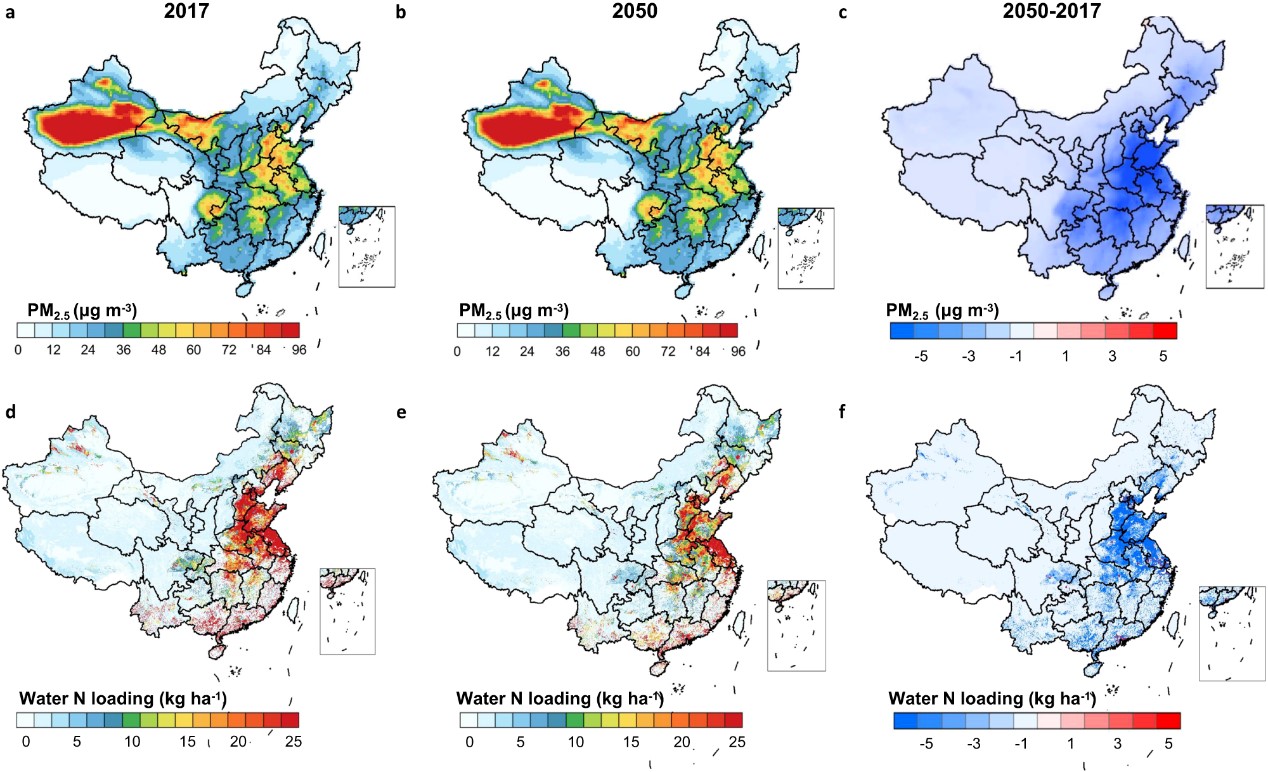
图 大气PM2.5浓度和海洋活性氮随城市化的空间变化
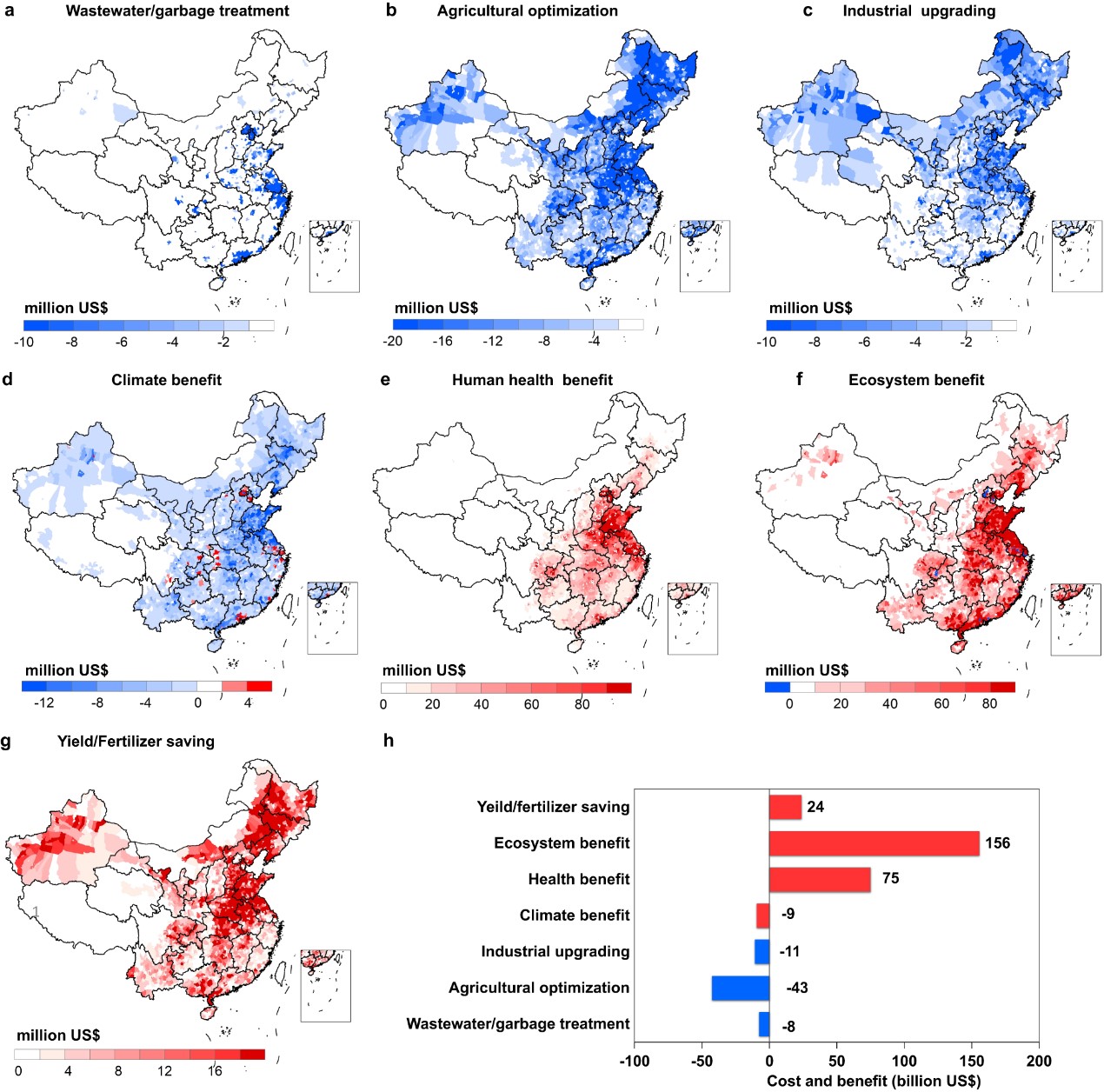
图 随着城市化将氮污染减半的成本和效益
原文链接:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-44685-y
节选转引:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/UDOuI5DoDQxtxEKYmSIH_g